On the same subject
“The triangle of death”
The clothes are then shipped to the European Union, the primary export market. While most Tunisians can afford to buy second-hand clothes on the so-called "fripes" markets, 82% of Tunisian textile production leaves the country, according to the latest figures published in a report by the NGO Avocats Sans Frontières. Tunisia, like Morocco and Egypt, are attractive destinations for textile manufacturing multinationals due to their geographical proximity to the European market.
Here, the tourist beaches quickly become a long, muddy marine expanse. The road that leads to the working-class neighborhoods south of Monastir, known as a hub of the textile industry - Khniss, Ksibet, Lamta, Ksar Hellal, Moknine - is paradoxically called Boulevard de l'Environnement (Environment Boulevard).
This street name can be found in every major city in the country as a symbol of the 'authoritarian environmentalism of Ben Ali's 1990s Tunisia' - as researcher Jamie Furniss called it - redeeming the image of dictatorship 'by appealing to strategic hot-button issues in the eyes of the "West."'
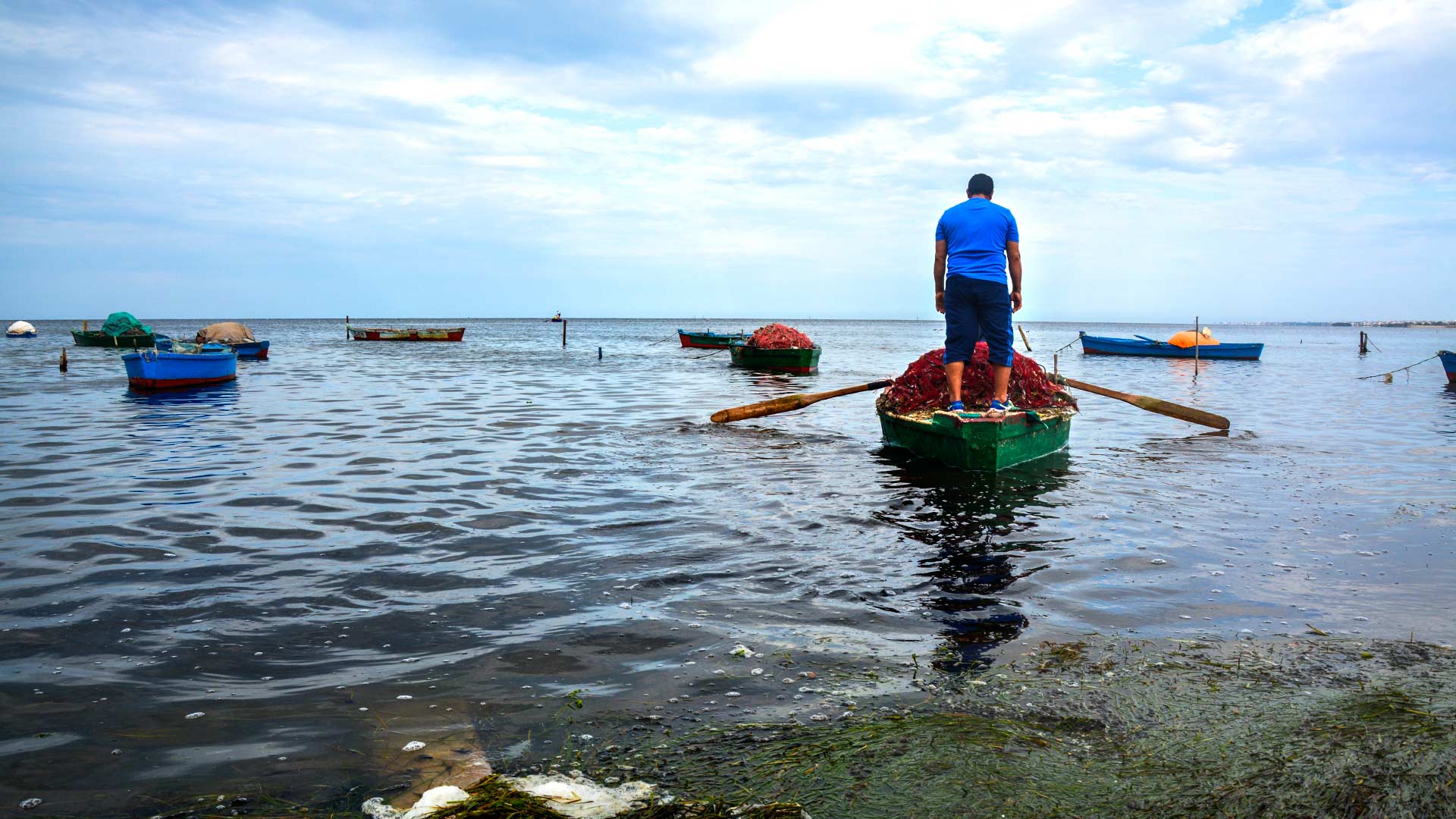
'As for us, we call this area the triangle of death,' tells a lone fisherman beside a small artisanal pier in Ksibet El-Mediouni, 13,000 residents.
After rolling up his pants, he dips his feet into the dirty water and climbs into a small wooden boat. 'Nowadays, to find even a tiny fish, we must move away from the coast.'
'Sadok is one of the last small fishermen who still dares to enter these waters,' confirms Yassine, a history professor in the city's public school, watching him from the main road to cope with the strong smell.
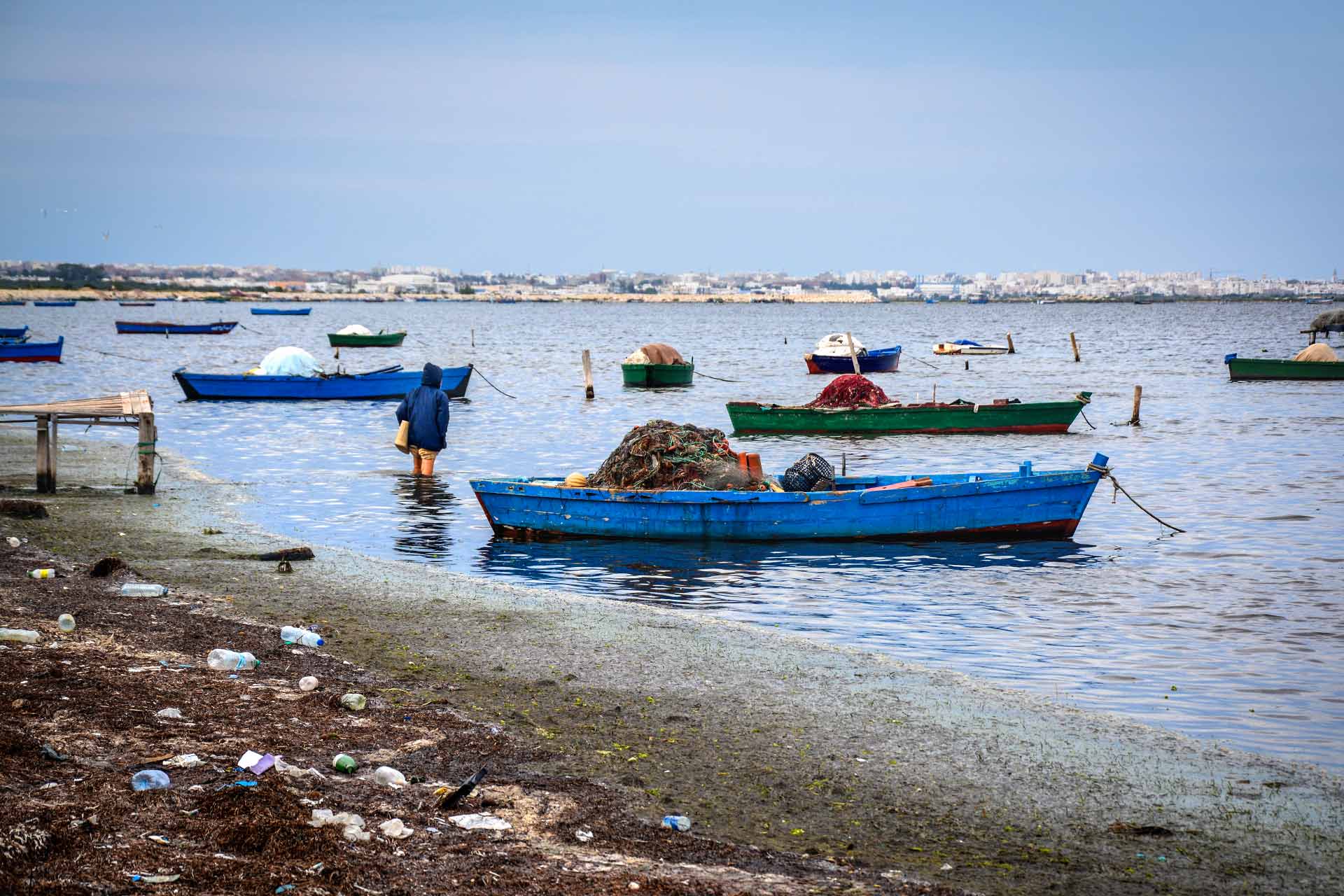

A fisherman walks to his boat in the bay of Ksibet El-Mediouni.
Passers-by of Boulevard de l’Environnement agree: the Ksibet El-Mediouni Bay died ‘because of an abnormal concentration of textile companies in a few kilometers’, they say, polluting the seawater where the population used to bathe in summer.
The region is home to five factory clusters. 'Officially, there are 45 in all, but there are illegal ones that we cannot count or even notice. They are often garages or warehouses without signs,' confirms Mounir Hassine, head of Monastir's Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights.
This is how the relocation of textile industries works: the big brands found in French, Italian, Spanish, and German shops relocate to Tunisia to cut costs. 'Then some local companies outsource production to other smaller, often undeclared companies to reduce costs and be more competitive,' explains Habib Hazemi, President of the General Federation of Textiles, Clothing, Footwear, and Leather in the offices of the trade union UGTT.
According to Hassine from the Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights (FTDES), ‘undeclared factories often dig wells to access groundwater and end up polluting the Bay by discharging wastewater directly into the sea’.
The public office responsible for water treatment (Office National de l'Assainissement, ONAS) 'fails to treat all this wastewater,' he adds, so State and private parties bounce responsibilities off each other'. 'The result is that nothing natural is left here,' Yassine keeps repeating.
'We are intoxicating fish, plants, and people. The only thing I can do is to teach my students what pollution is and hope they can find a way to leave.'
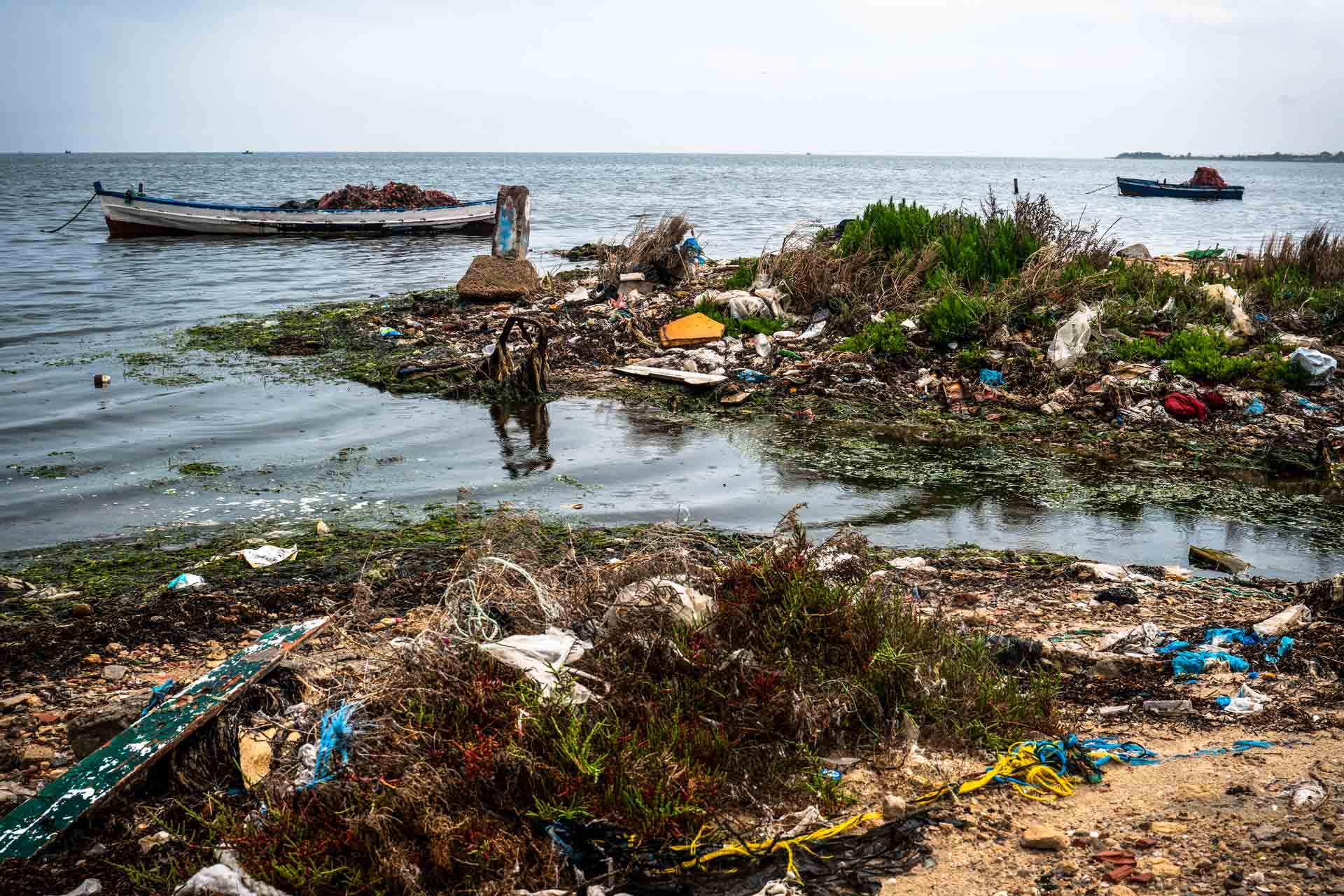

A river flows into the sea from an industry near the port of Ksibet.
The unheard call of civil society
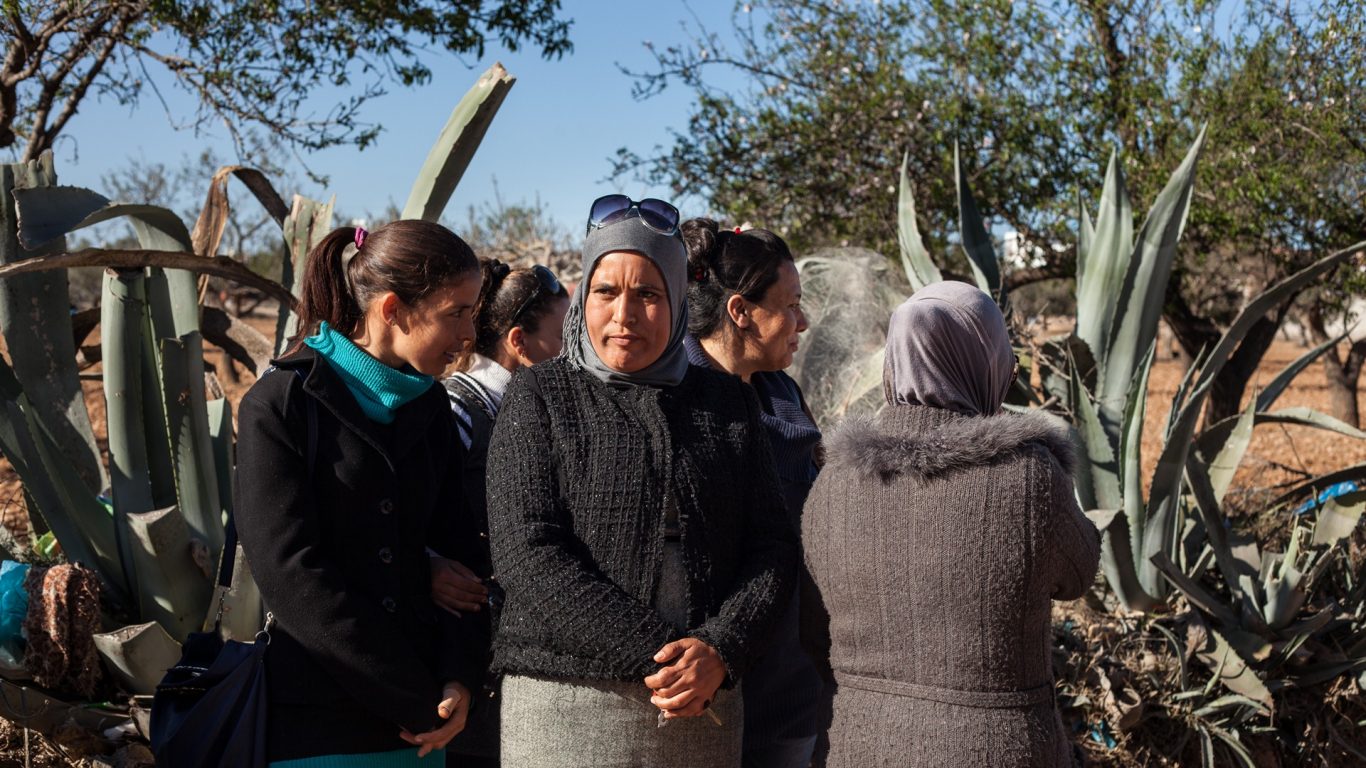
Fatma Ben Amor, 28, has learned the meaning of pollution by looking at it through her window and listening to the stories of her grandparents, born and raised in the small town of Ksibet El Mediouni. ' They often tell me that people used to bathe and go fishing here. I never knew the 'living' beach,' says this local activist.
After the revolution, her city became the center of a wave of protests in 2013 by the population against 'an ecological and health disaster,' it was written on the protesters' placards. Nevertheless, the protests yielded no results, and marine pollution has continued.
On the same subject
Founded in 2014, the Association for the Protection of the Environment in Ksibet el Mediouni (APEK) monitors the level of marine pollution in the so-called 'triangle of death.' Fatma tries to raise awareness in the local community: 'We began with a common reflection on resource management in the region and the idea of reclaiming our bay. Here, youth are used to the smells, the waste, the dirty sea.'
Under one of the bridges on Boulevard de l'Environnement runs one of the few rivers where there is still water. That water, however, ‘gathers effluent from the area's industries’, the activists complain. 'The water coming from Oued el-Melah, where all the factories unload, pollutes the sea,' she explains by pointing to the oued.
According to the latest report by Avocats Sans Frontières (ASF) and FTDES in August 2023, one of the leading causes of marine pollution in Monastir governorate would be the denim washing process, a practice used in the dyeing of jeans.
'11 million pairs of jeans were exported to the EU in 2022 [from Tunisia alone], 85% after getting the denim washing process. You need between 55 and 72 liters of water for a pair of jeans,' Mounir Hassine FTDES Monastir reports.
The ASF research explains that the jeans sector is characterized by technical processes involving chemicals - such as acetic acid used for washing, several chemical detergents and bleaching products, or hydrogen peroxide - and massive water consumption in a country suffering from water stress.
During the period of 2011-2022, Tunisia has ratified important international texts that will strengthen and enrich Tunisian national law in terms of pollution control, environmental security, and sustainable development. ' Although the regulations governing environmental protection and the use of water resources are strict, the authorities in charge of controls and prosecutions are outdated and unable to deal with the infringements,' the ASF report confirms.
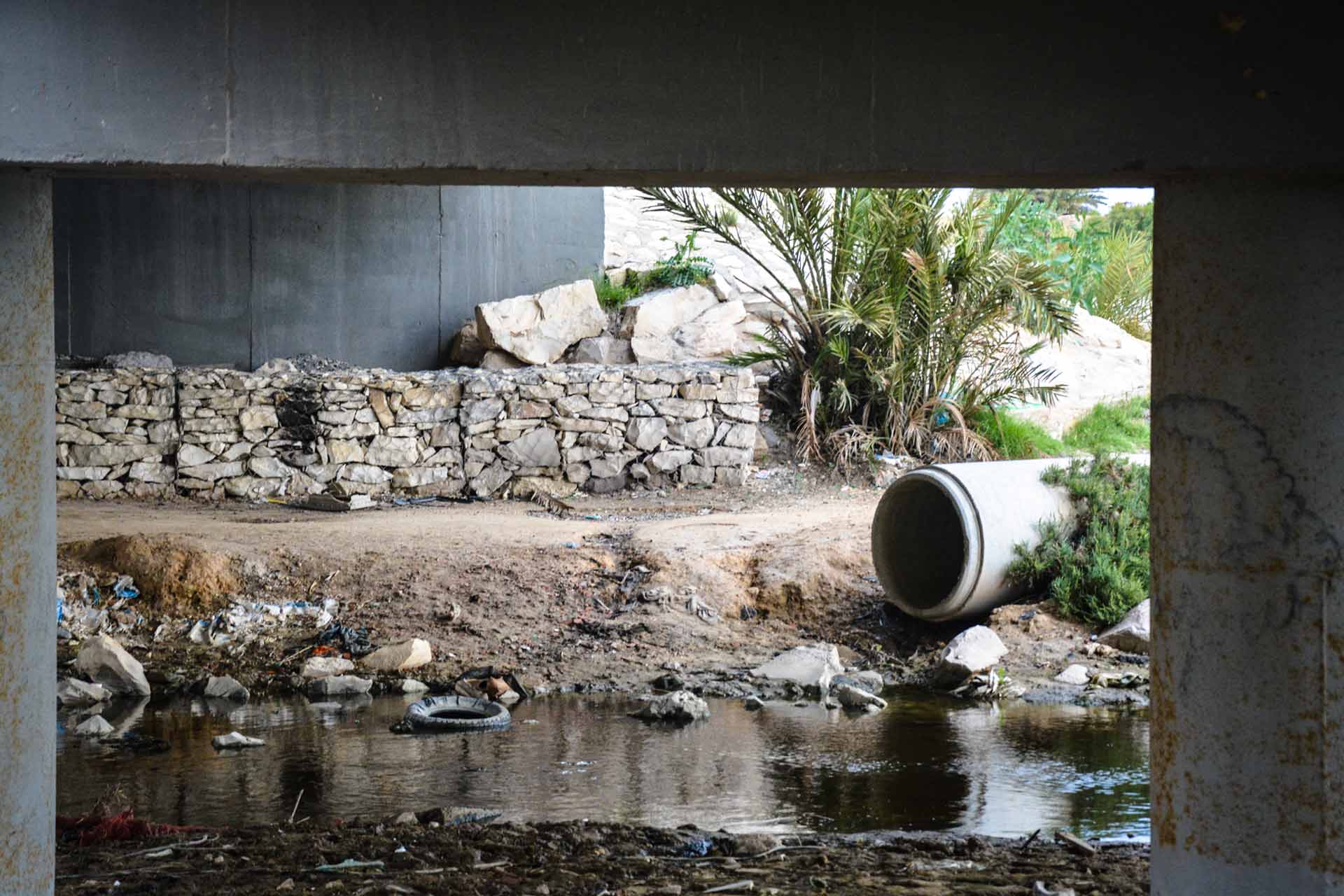

Under the bridge over Oued el-Melah, the polluted river that flows into the sea.
According to both civil society organizations, there are mainly two sources of pollution in Ksibet Bay: polluting industries discharging chemicals directly into the seawater and the Office de l'Assainissement (ONAS) , 'which should be responsible for treating household wastewater, but mainly manages wastewater from factories discharging, and then throw them into the sea,' Fatma Ben Amor explains.
'Take, for example, the ONAS plant at Ouad Souk, in Ksibet Bay. Created in 1992, it has a treatment capacity of 1,680 cubic meters per day, with a population more or less adapted to this capacity. It receives more than 9,000 cubic meters daily on average,' Mounir Hassine confirms.
ONAS did not respond to our interview requests. The Tunisian Textile and Clothing Federation (FTTH), representing part of the sector's employers, assures that ‘the large companies in the region have all the necessary certifications and now use a closed cycle that allows water to be reused.’ The FTTH adds that the sector is taking steps towards the energy transition and respect for the environment.
UTICA Monastir, the other branch of the employers' association, has also confirmed this information. While a system of certifications and environmental audits has been put in place to monitor the work of large companies, ‘the underground part of the production chain escapes the rules,’ admits one entrepreneur anonymously.
Remains of waste in the bay of Ksibet El-Mediouni.
‘This pair of jeans is water’
ONAS finds itself treating more water than the treatment stations' capacities because, within a few decades, the Monastir region has radically changed its economic and resource management model. A few kilometers from the towns on the coast, roads run through olive groves that recall the region's agricultural past.
But today, agriculture and fishing are also industrialized: the governorate of Monastir produced almost 20,000 tonnes of olive oil by 2020. With 14 aquaculture projects far from the coast, the region ranks first in fish production, with an estimated output of between 17,000 and 18,000 tonnes by 2022.
A wave of drought in the 1990s intensified the rural exodus from inland Tunisia to the coast. 'This coastal explosion has been accompanied by a development model that looked to globalization rather than domestic needs,' Mounir Hassine from FTDES explains. 'Our region has been at the heart of so-called vulnerable investments, which bring in cheap labor without considering environmental needs and rights.'
This sudden increase in residents has put greater pressure on the region's natural water resources, ‘which supply only 50% of our water needs,' he adds. The remaining 50 percent comes from the increasingly empty northern Oued Nebhana and Oued Medjerda dams. However, much of the water resources are not used for household needs but for industrial purposes.
According to the ASF report, export companies draw their water partly from the public drinking water network (SONEDE). But the primary source is wells that draw water directly from the water table: 'Although the water code regulates the use of wells, 70% of the water used by the textile industry comes from the region's unauthorized groundwater'. 'Most wells are dug inside the factories,' Mounir Hassine from FTDES confirms.
Due to the current drought wave and mismanagement of resources, Tunisia is now in water poverty, with an average use of 450 cubic meters of water per citizen (the poverty line is 500), according to 2021 data. Moreover, the Regional Agricultural Commission figures show that the water level in Monastir's aquifers falls between three and four meters yearly.
Water mismanagement is not just a problem in the textile industry. This type of production, however, is highly water-hungry, especially when it comes to the denim washing process.
'We are part of an extended supply chain: a pair of jeans sold for 10 euros costs the company 30 cents here. The export price does not take water into account, a huge loss of revenue for the State,' observes Zeyneb Mrouki from Avocats Sans Frontières. 'This pair of jeans is water.'
Even if the big brands are at the top of the production chain that ends on the coast of Ksibet El Medeiouni, ‘ they will rarely be held accountable for the social and environmental damage they leave behind,’ admits an entrepreneur in the sector working in subcontracting. Tunisian companies all work for several brands at the same time, and they don't carry the same name as the big brands, which outsource production.
‘Tracing the chain of responsibility is complicated, if not impossible,’ confirms Adel Tekaya, President of UTICA Monastir.
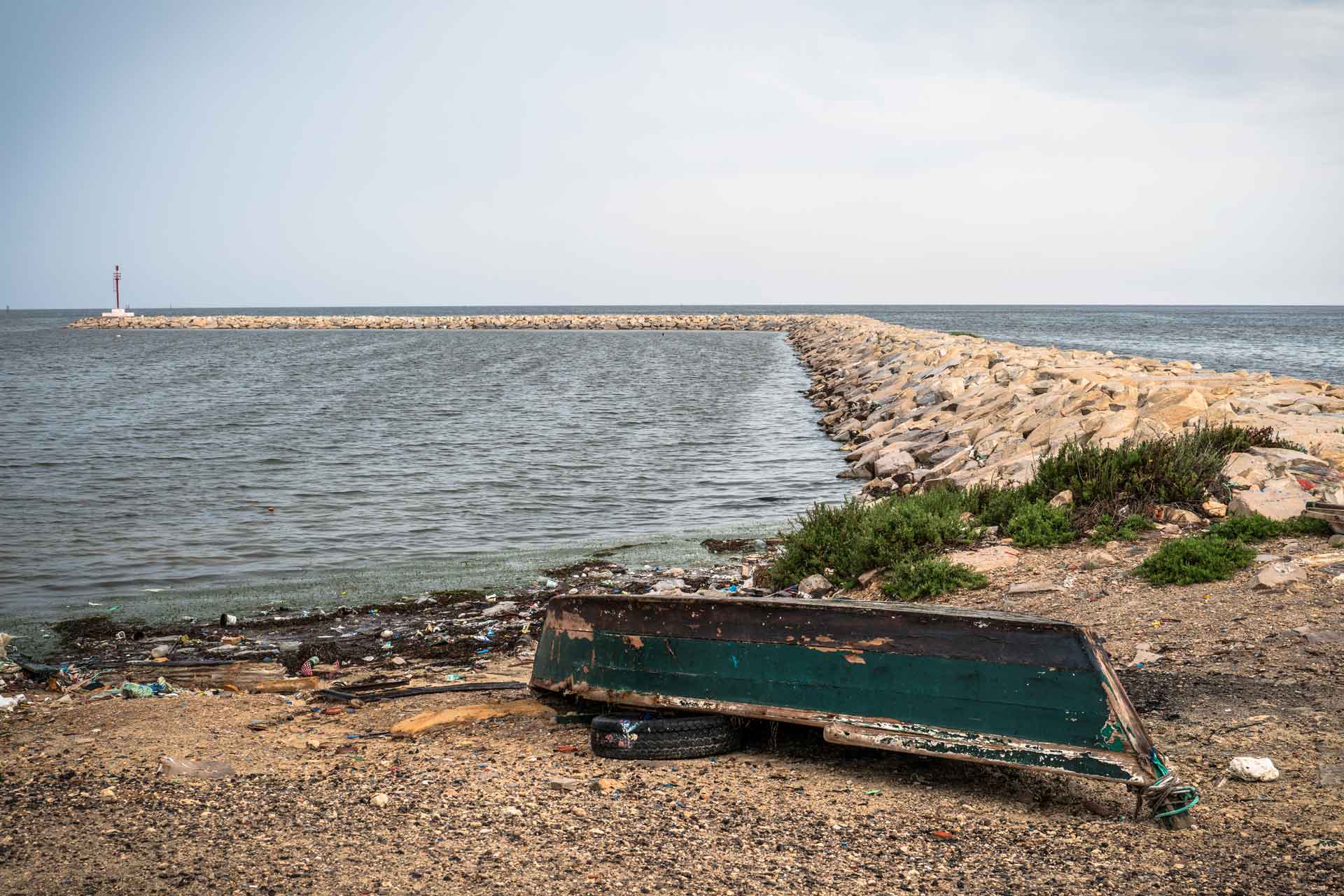

The port of Ksibet El-Medeiouni is empty despite the bad weather.
The EU wants to produce more green but continues to relocate South
Once taken directly from the aquifer or from the public drinking water company, SONEDE, a part of the waters polluted by chemical processes, thus ends up in the sea without being filtered. According to scholars, textile dyeing is responsible for the presence of 72 toxic chemicals in water, 30 of which cannot be eliminated.
According to the World Bank, between 17% and 20% of industrial water pollution worldwide is due to the dyeing and finishing processes used in the textile industry. A figure confirmed by the European Parliament states:
“Textile production is estimated to be responsible for around 20% of global clean water pollution from dyeing and finishing products".
The EU has set itself the target of achieving good environmental status in the marine environment by 2025 by applying the Marine Strategy Framework Directive. Still, several polluting sectors continue to relocate their production to the Southern countries, where ‘there are fewer controls and costs,' explains the entrepreneur requesting anonymity for fear of consequences for criticizing a 'central sector' in the country.
But pollution knows no borders in the Mediterranean. 87% of the Mediterranean Sea remains contaminated by chemical pollutants, according to the first map published by the European Environment Agency (EEA), based on samples taken from 1,541 sites.
The environmental damage of the textile industry - considered one of ‘the most polluting sectors on the planet’ - was also addressed at Cop27 in Sharm El-Sheikh, where a series of social and climate objectives concerning greater collaboration between the EU and the MENA region were listed.
One of the main topics was the urgent harmonization of environmental standards in the framework of the installation of digital product passports', a tool that will track the origin of all materials and components used in the manufacturing process.
FTTH ensures that large companies on the Monastir coast have invested in a closed water re-use cycle to avoid pollution. ‘All companies must invest in a closed loop that allows water reuse,’ Mounir Hassine reiterates.
But to invest in expensive and reconversion work requires a long-term vision, which not all companies have. After a period of ten years, companies can no longer benefit from the tax advantages guaranteed by Tunisian investment law. ‘Then they relocate elsewhere or reopen under another name,’ Mounir Hassine adds.
Environmental and health damages of marine pollution
Despite the damage, only female workers walking around in white or colored uniforms at the end of the working day prove that the working-class towns south of Monastir constitute the most important manufacturing hub of Made In Tunisia clothes production. The sector employs 170,000 workers in the country.
On the same subject
Tunisia is the ninth-largest exporter of clothing from the EU, after Cambodia, according to a study by the Textile Technical Centre in 2022. More than 1,530 companies are officially located there, representing 31% of the national fabric. 82% of this production is exported mainly to France, Italy, Belgium, Germany, and Spain.
Some women sit eating lunch not far from warehouses on which signs ending in -tex. Few dare to speak; one of them mentions health problems from exposure to chemicals. 'We have received complaints about health problems caused by the treatment and coloring of jeans,' confirms FGTHCC-UGTT (Textile, Clothing, Footwear and Leather Federation) general secretary Habib Hzemi. Studies have also shown that textile workers – particularly in the denim industry – have a greater risk of skin and eye irritation, respiratory diseases, and cancer.
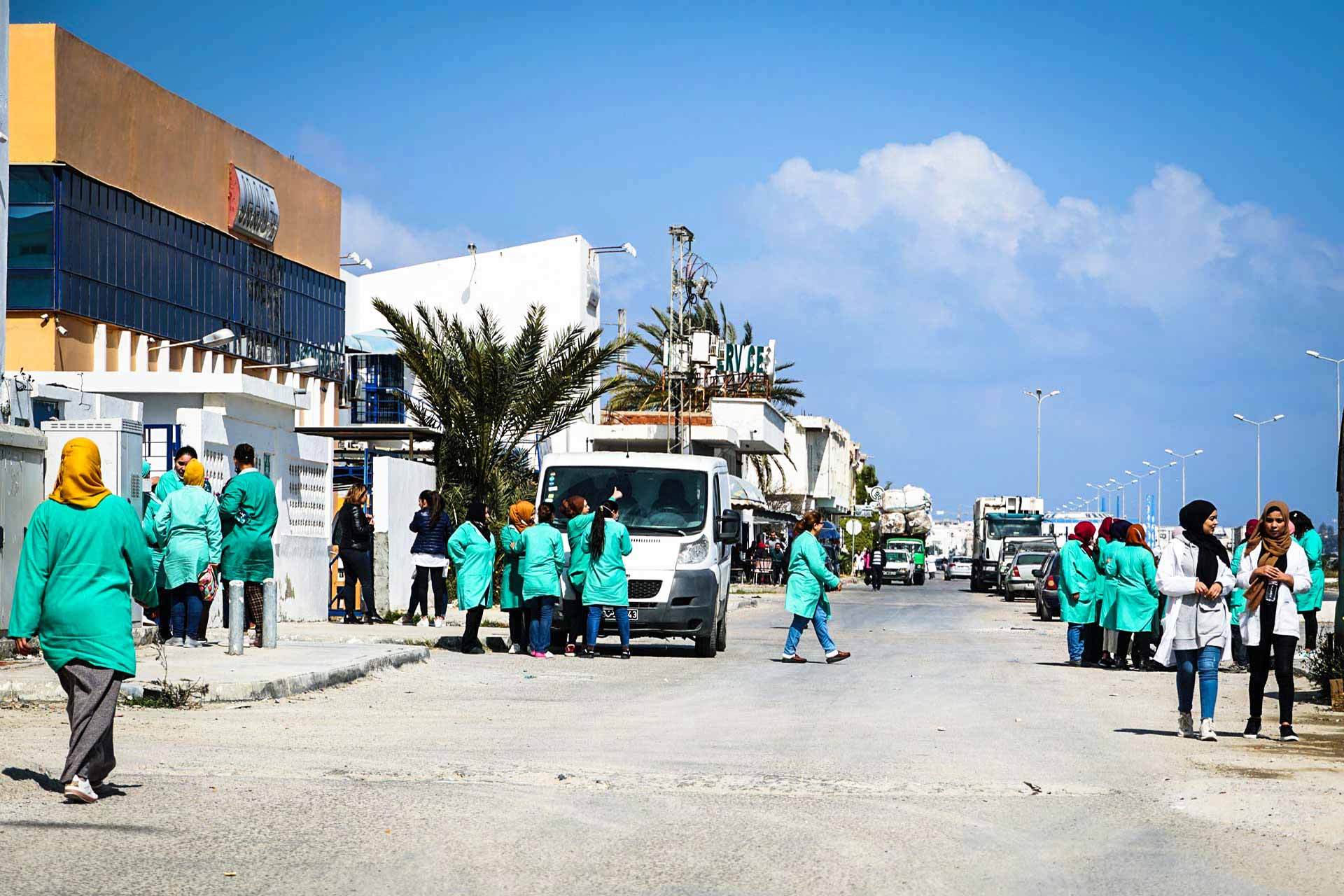

Workers on their lunch break in front of one of the many businesses located along the Boulevard de l'environnement, which runs through the southern suburbs of Monastir.
Pollution, however, affects not only the textile workers but the entire community of Ksibet. 'We do not know what is in the seawater, and many of us prefer not to know. We have tried to get laboratory tests, but they are very expensive,' explains Fatma Ben Amor of the APEK Association.
'What we do know is that we all have a family member here with cancer.'
'According to an opinion poll by the Association for the Protection of the Environment of Ksibet Mediouni (APEK) in July 2016, the cancer rate is 4.3%. Among the highest rates worldwide,' explains a study on cancer in Ksibet for the German Heinrich Böll Stiftung. Different carcinogenic diseases have been reported in the local community, but a cancer register has never been set up.
Pollutants from the textile industry have impacted marine life too. Like all towns on the coast, Monastir is known for fishing bluefish, sea bream, cod, and other Mediterranean species. But artisanal fishing is increasingly complicated in front of the bay of Ksibet El Mediouni, and the sector has become entirely industrialized. Thus, the town's small port is deserted.
'The port of Ksibet is emptying out, while the ports of Sayeda and Teboulba, beyond the bay, are still working. There are only a few small-scale fishermen left. We used to walk into the water to catch octopuses with our hands,' one of the port laborers explains anonymously, walking on the Bay.
'Thirty years ago, this was a nursery for many Mediterranean species due to the shallow waters. Now, nothing is left,' he adds. As confirmed by several fishermen in the area, the population has witnessed several fish deaths, most recently in 2020.
'We sucked up the algae, waste, and chemical waste a few years ago for maintenance work,' explains the port laborer. 'Once we cleaned it up, the sea breathed again. For a few days, we saw fish again that we had not seen for years. Then the quicksand swallowed them up again.'
This story was produced with support from Internews’ Earth Journalism Network







